Python set difference() Explained with Full Step-by-Step Solution
Problem statement
Input format
- First line: number of students who subscribed to the English newspaper (n)
- Second line: n space-separated roll numbers for English subscribers
- Third line: number of students who subscribed to the French newspaper (m)
- Fourth line: m space-separated roll numbers for French subscribers
Output format
- A single integer, the number of students who have subscribed only to the English newspaper
Example
Input
9
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
9
10 1 2 3 11 21 55 6 8
Output
4
Explanation
English-only roll numbers are 4, 5, 7, 9. There are four of them.
Key idea
- Use Python sets to remove duplicates and to run set operations quickly.
- The set difference operation returns items in one set that are not in another.
- If the English set is
Eand the French set isF, thenE.difference(F)gives students who subscribe only to English. - The result size is
len(E.difference(F)).
Why sets?
- Membership checks in sets are fast.
- Sets remove repeated roll numbers automatically.
- Set operations are simple and expressive.
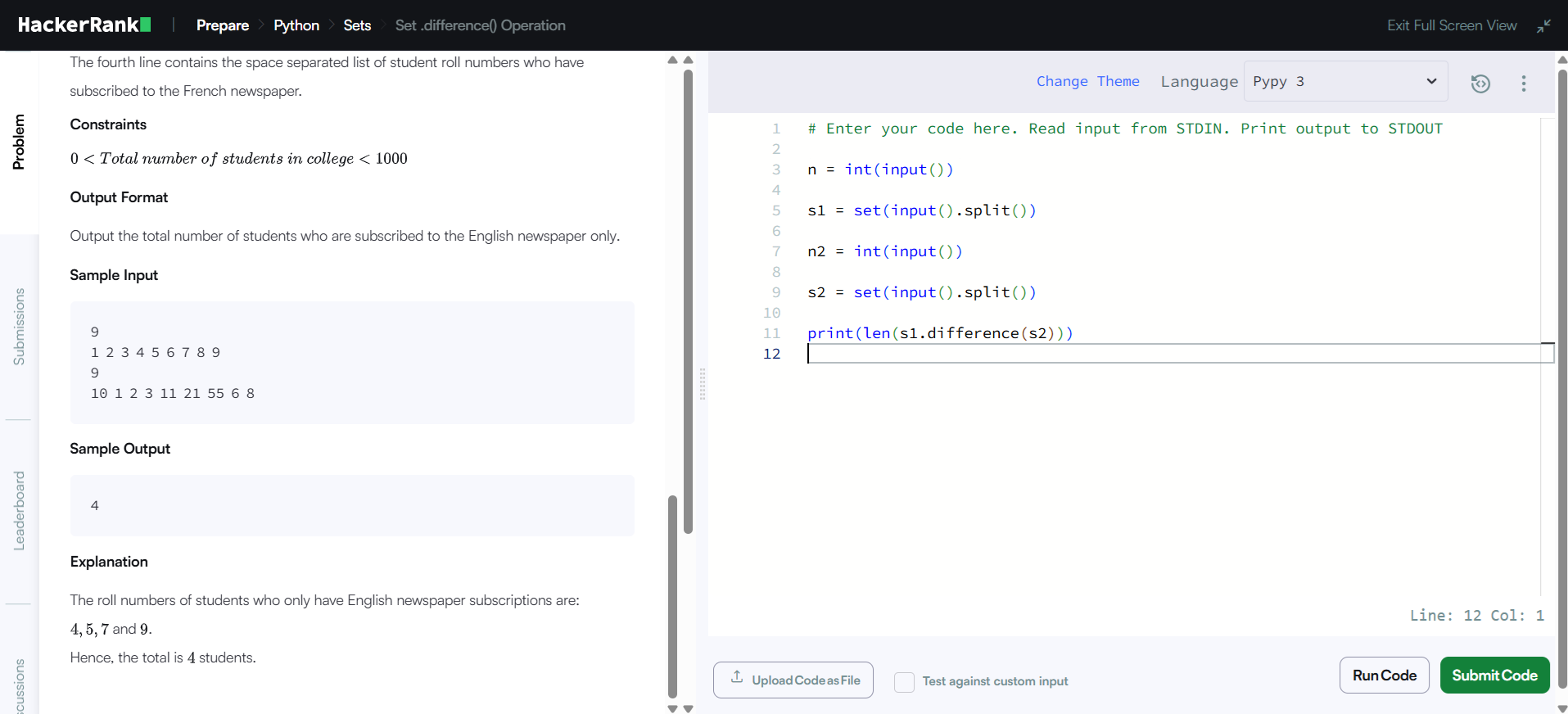
Python set difference solution
# read number of English subscribers (not used directly)
n = int(input())
# read English roll numbers and make a set
s1 = set(input().split())
# read number of French subscribers (not used directly)
n2 = int(input())
# read French roll numbers and make a set
s2 = set(input().split())
# print number of students who subscribed only to English
print(len(s1.difference(s2)))
Line-by-line explanation of Python set difference
n = int(input())- Reads the first line. It is the count of English subscribers. We parse it to an int. The program does not require this number later, but the input includes it. Reading it keeps the input alignment correct.
s1 = set(input().split())- Reads the second line.
input().split()Returns a list of roll-number strings separated by space. set(...)converts the list to a set. This removes duplicates and gives O(1) average membership checks.
- Reads the second line.
n2 = int(input())- Reads the third line, the count of French subscribers. It is parsed to int. It is not used later, but it moves input reading to the correct place.
s2 = set(input().split())- Reads the fourth line and converts it to a set for the same reasons.
print(len(s1.difference(s2)))s1.difference(s2)Returns a new set containing elementss1that are not ins2.len(...)gives the number of such elements.print(...)outputs the final answer.
Alternate syntax: s1 - s2 gives the same result as s1.difference(s2) for sets. Use either for clarity.
- Small tests you can try for Python set difference
- No overlap
1. Input
3
1 2 3
2
4 5
1. Output
3
- All overlap
2. Input
4
1 2 3 4
4
1 2 3 4
2. Output
0
- Duplicates in input lines
3. Input
6
1 2 2 3 3 4
3
3 4 5
3. Output
2
Explanation: English set becomes {1,2,3,4}. After removing {3,4,5}, only {1,2} remain.
Common mistakes and tips
- Treat roll numbers as strings if they include leading zeros. Converting to int will drop leading zeros. Use
split()and leave values as strings if roll numbers may have leading zeros. - Do not assume the line counts must match the actual number of items. Always read the count lines to keep input alignment.
- Using lists only will make membership checks slow for large inputs. Use sets for speed.
s1.difference(s2)Returns a new set. It does not changes1. If you want to updates1in place, uses1.difference_update(s2).
Learn more about Python’s official documentation on Python.org.
Visit YouTube to View the Complete Solution
Check out my YouTube tutorial, where I run and walk through this exact code in real time, if you want a step-by-step video explanation.
Related Post:
Integers Come in All Sizes HackerRank Python Solution
Power Function HackerRank Solution Explained in 5 Simple Steps
Final notes
- The solution is short and fast.
- Sets give clean semantics for subscriptions and duplicates.
- Use
len(s1.difference(s2))orlen(s1 - s2)to get the final count.
Conclusion
Data science is transforming finance, from predictive analytics to personalised services. It’s not just a technology upgrade – it’s changing how the industry operates. Those who leverage data science will stay ahead in this data-driven era.
Want to explore more? Join our free Masters in Data Science with Power BI workshop at ConsoleFlare. Learn each tool and technology from scratch, understand the field deeply, and become job-ready for data science roles.
Why ConsoleFlare?
-
Recognised as one of the Top 10 Most Promising Data Science Training Institutes 2023
-
Learn in Hindi, in a way that’s easy to grasp
-
Curriculum focused on what you need to learn, nothing extra
Register now, and our team will call you back to get you started.




