Power Function HackerRank Solution Explained in 5 Simple Steps
The power function in Python is the main idea behind this HackerRank challenge. In this problem, you work with exponents and modulus, and Python provides a clean way to handle both. This guide walks you through the full HackerRank Power Function solution in five simple steps so that each line makes sense.
This tutorial also shows how the power function works with and without modulus, helping you solve every test case correctly. By the end, you will feel confident running the code yourself.
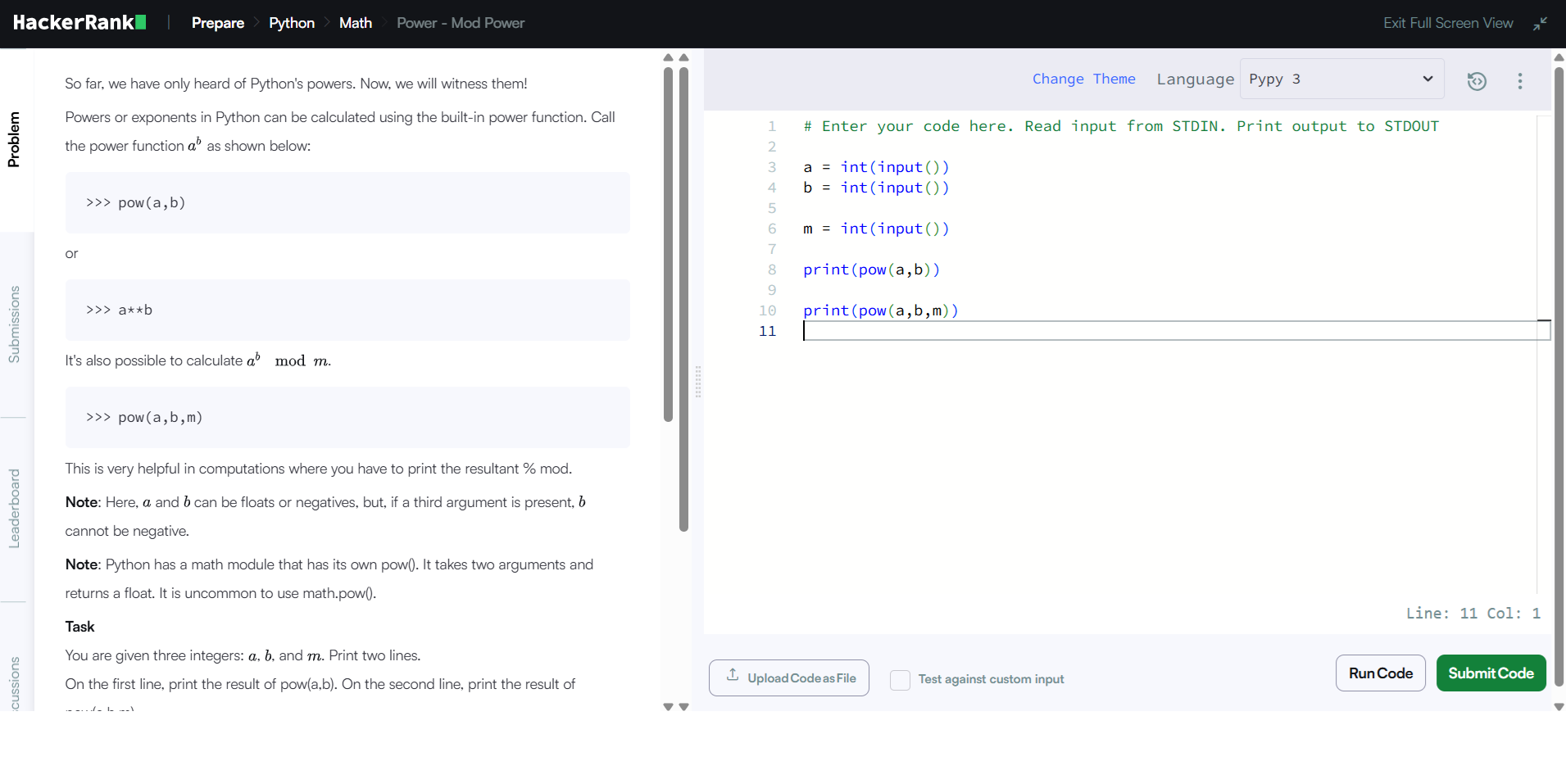
Step 1
Understand basic power operations
You raise a number to an exponent. Python gives you two ways.
-
a ** b pow(a, b)
Both return the same value.
Python multiplies the number repeatedly inside the function.
If the exponent is zero, the result is always 1.
If the exponent is negative, Python returns a float because it turns the operation into division.
Example:
3 ** 4 gives 81pow(3, 4) also gives 81
A common mistake is expecting an integer when the exponent is negative. Negative exponents always produce a float.
Keep your inputs positive if you want clean integer results.
Step 2
Learn how pow(a, b, m) works
The third argument adds a modulus.
This version of the function calculates (a ** b) % m in an efficient way.
Python does not compute the full value a ** b when it becomes huge. It reduces the number at each step to keep it small. This makes your code fast and safe.
Example
pow(3, 4, 5)gives 1
3 raised to 4 is 81
81 mod 5 is 1
Do not use a negative value for the modulus. Python does not accept it when the third argument is present.
Use the three-argument version whenever you work with big exponents or when the challenge expects a modulus.
Step 3
Read the input in the right order
HackerRank gives you three integers on separate lines.
First line: a
Second line: b
Third line: m
Read them one by one and convert them to integers.
Follow the given order, or your output will be wrong.
Example input
3
4
5A common mistake is changing the order or adding extra steps that are not needed.
Read the values directly and keep the flow simple.
Step 4
Check the sample input to confirm your logic
Use the sample test to verify your understanding.
Input
3
4
5Processpow(3, 4) → 81pow(3, 4, 5) → 1
Expected output
81
1This test shows that your logic is correct.
Make sure your output matches exactly.
No extra text. No extra spaces. No blank lines.
Even a small extra print will cause a wrong answer on HackerRank.
Step 5
Write the final solution and test edge cases
The final code is short and clean.
Test a few extra cases in your mind.
-
If b is zero, the result is 1
-
If a is zero and b is positive, the result is 0
-
A negative exponent returns a float
-
Large exponents run safely with the modulus version
Avoid using math.pow() because it returns a float and loses accuracy.
The built-in It pow() is designed for integer operations and works better here.
Learn more about Python’s official documentation on Python.org.
Visit YouTube to View the Complete Solution
Check out my YouTube tutorial, where I run and walk through this exact code in real time, if you want a step-by-step video explanation.
Related Post:
Mod Divmod in Python Explained with Simple Examples | HackerRank Problem
HackerRank Collections.deque() Solution in Python
Conclusion
Data science is transforming finance, from predictive analytics to personalized services. It’s not just a technology upgrade – it’s changing how the industry operates. Those who leverage data science will stay ahead in this data-driven era.
Want to explore more? Join our free Masters in Data Science with Power BI workshop at ConsoleFlare. Learn each tool and technology from scratch, understand the field deeply, and become job-ready for data science roles.
Why ConsoleFlare?
-
Recognized as one of the Top 10 Most Promising Data Science Training Institutes 2023
-
Learn in Hindi, in a way that’s easy to grasp
-
Curriculum focused on what you need to learn, nothing extra
Register now, and our team will call you back to get you started.




